Archive for category: ASTM Test
ASTM E283 – 04 (2012) 공기누설 시험
[공기누설특성 시험]
ASTM E283 – 04(2012) Standard Test Method for Determining Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Specimen
ASTM E 84 시험안내
연소특성시험
ASTM E 84 – Surface Burning Characteristics-Fire safety technology
표면연소 특성이란?
재료의 표면연소 특성은 연기생성을 제한하고 동시에 화염에 저항하는 능력을 종합적으로 평가하는 것으로써 보통 건축법이나 기타 정부등의 기관에서 규정한다.
내부 벽이나 천장 마감 재료로 사용되는 재료에 있어서 화염 전파율은 중요한 물리적 특성 중에 하나이다.
통제된 화재 조건에서 상대적으로 표면 연소 특성을 결정하기위한 표준적인 시험방법은 수평 화재 터널 장치(Steiner Tunnel)를 이용하는 ASTM E 84이다. 이 방법은 비록 두 측정이 직접적 연관이 적을 수 있지만, 화염의 확산 및 연기의 확산 지수를 결정하고, 특정설치요구사항에 대한 재료의 적용성을 결정하는데 도움이된다.
시험 방법
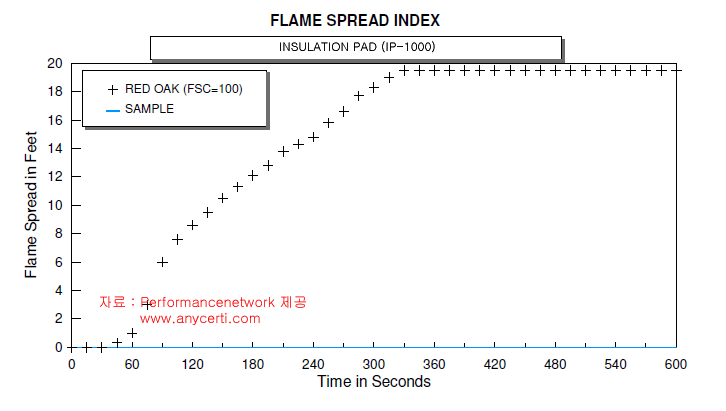
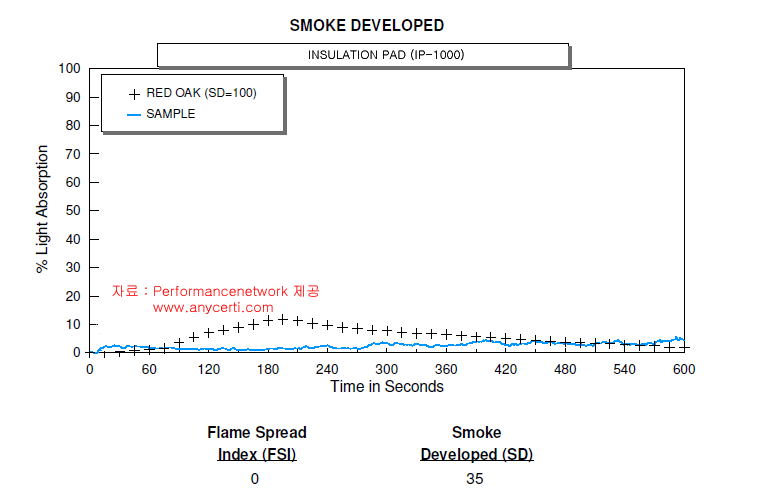
ASTM E 84 ; 건축 자재의 표면연소 특성에 대한 시험표준 방법에 지정된 스타이너 터널은 특정한 시험 조건하에서 물질의 상대적 표면연소 특성을 결정하기 위해서 설계되었습니다. 시험의 결과는 화염확산 지수( FSI )와 연기발생(SD) 지수로 표현됩니다.
이 스타이너 터널은 규정된 특정한 온도로 예비 가열하고 또 사전시험온도로 냉각이 허용되며 12인치 폭과 24피트 길이의 터널뚜껑을 열고 시료를 설치할 수 있도록 되어 있다. 터널 천정에 설치되는 시험편은 장치의바닥을 향해 설치된다. 뚜껑이 덮여지고 버너를 점화하여 시편의 한쪽에서 불꽃을 인가한다. 화염확산 거리를 관찰하고 10분 이상동안 매초마다 확산거리를 기록하고 레드 오크(임의로 할당된 100에 대한 FSI 및 SD )의 비교치에 근거한 FSI 및 SD 를 결정하기 위하여 계산이 이루어진다 .
테스트 결과
ASTM E 84에는 등급기준이 포함되어 있지 않습니다. 그러나, 많은 업계 문서는 ASTM E 84 테스트 데이터를 참조 하고 일반적 등급기준을 적용합니다. 비록 각 문서에서 사용되는 용어가 서로 다를 수 있지만 등급범위는 일반적으로 동일하다.
일반적인 범위 :
클래스 A 또는 클래스 1 ( FSI = 0-25 )
클래스 B 또는 클래스 2 ( FSI = 26-75 )
클래스 C 또는 클래스 3 ( FSI = 76-200 )
위 모든 각 분류는 최대 450의 연기발생(SD )율을 규정함
Test Result (Red Oak Referenced)
아래는 ASTM E84 시험결과표현 방법사례입니다.
테스트 실시 시기
ASTM E 84는 제품 개발 단계나 지속적인 기업 품질 보증 프로그램의 일부로 이용 될 수있다. 특히 북미와 중동의 많은 글로벌 관할권역의 건물관리는 내부 벽 및 천정 마감 재료에 대해 ASTM E 84를 강제하고 있고 나아가 지역별 기관의 강제요건에 따라 이들 재료에 대한 일회시험 반복시험, 확장시험(예 :30 분), 또는 더 집중적인 제품 인증 프로그램의 시험항목을 적용한 시험의 결과가 적용되어질 수 있다 .
시료 요구 사항
각 시험에서는 폭 21인치(533mm), 길이24피트(7,315mm)의 시료가 요구된다 (예:각 21인치 폭(533mm), 8 피트 길이(2,438mm)의 시료 3개가 필요). 시료의 두께가 3 인치(75mm) 미만 또는 6 인치 (150mm )보다 두꺼운 경우, 터널 뚜껑을 수정해야 표준시험을 할 수 있으며 유리 섬유 강화 시멘트 보드 또는 석고 보드가 일반적인 기판으로 사용되어 질 수 있다. 그 외 세부 내용은 시험소의 설비의 조건을 고려하여야 한다.
TEST PROCEDURE
ASTM E 84-13a
-”Standard Method of Test for Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials”
ASTM E 84-13a “건축 자재의 표면 연소 특성에 대한 표준 시험 방법”으로 지정된이 방법은 특정 시험 조건 하에서 재료의 상대적인 표면 연소 특성을 결정하도록 작성되었습니다. 시험의 결과는 화염 확산 지수 (FSI) 및 연기 발생 (SD)으로 표현되며 화염 데이터의 비교 표면 확산을 개발하기 위해 건축에 사용되는 재료, 제품 및 조립품에 이 시험방법이 적용 가능하지만, 시험 결과는 모든 건축 화재 조건에서 시험 된 물질의 상대적인 표면 연소 특성을 반영하지 않을 수 있습니다. 따라서 시험대상 및 시험목적 등을 고려한 시험조건을 검토하여야 합니다.
화재관련 규격 및 시험
ASTM & STP
- ASTM D2898-10 Standard Practice for Accelerated Weathering of Fire-Retardant-Treated Wood for Fire Testing
- ASTM D5425-13 Standard Guide for Development of Fire Hazard Assessment Standards of Electrotechnical Products
- ASTM D5664-10 Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Effects of Fire-Retardant Treatments and Elevated Temperatures on Strength Properties of Fire-Retardant Treated Lumber
- ASTM D6113-11 Standard Test Method for Using a Cone Calorimeter to Determine Fire-Test-Response Characteristics of Insulating Materials Contained in Electrical or Optical Fiber Cables
- ASTM D6513-08 Standard Practice for Calculating the Superimposed Load on Wood-frame Walls for Standard Fire-Resistance Tests
- ASTM E108-11 Standard Test Methods for Fire Tests of Roof Coverings
- ASTM E119-12a Standard Test Methods for Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials
- ASTM E1355-12 Standard Guide for Evaluating the Predictive Capability of Deterministic Fire Models
- ASTM E1537-13 Standard Test Method for Fire Testing of Upholstered Furniture
- ASTM E1546-09a Standard Guide for Development of Fire-Hazard-Assessment Standards
- ASTM E1590-13 Standard Test Method for Fire Testing of Mattresses
- ASTM E1591-13 Standard Guide for Obtaining Data for Fire Growth Models
- ASTM E1678-10 Standard Test Method for Measuring Smoke Toxicity for Use in Fire Hazard Analysis
- ASTM E176-13 Standard Terminology of Fire Standards
- ASTM E1776-13 Standard Guide for Development of Fire-Risk-Assessment Standards
- ASTM E1822-12 Standard Test Method for Fire Testing of Stacked Chairs
- ASTM E2032-09(2013) Standard Guide for Extension of Data From Fire Resistance Tests Conducted in Accordance with ASTM E 119
- ASTM E2058-13a Standard Test Methods for Measurement of Material Flammability Using a Fire Propagation Apparatus (FPA)
- ASTM E2061-12 Standard Guide for Fire Hazard Assessment of Rail Transportation Vehicles
- ASTM E2174-10ae1 Standard Practice for On-Site Inspection of Installed Fire Stops
- ASTM E2257-13a Standard Test Method for Room Fire Test of Wall and Ceiling Materials and Assemblies
- ASTM E2280-13 Standard Guide for Fire Hazard Assessment of the Effect of Upholstered Seating Furniture Within Patient Rooms of Health Care Facilities
- ASTM E2307-10 Standard Test Method for Determining Fire Resistance of Perimeter Fire Barriers Using Intermediate-Scale, Multi-story Test Apparatus
- ASTM E2336-04(2013) Standard Test Methods for Fire Resistive Grease Duct Enclosure Systems
- ASTM E2393-10a Standard Practice for On-Site Inspection of Installed Fire Resistive Joint Systems and Perimeter Fire Barriers
- ASTM E2574/E2574M-12a Standard Test Method for Fire Testing of School Bus Seat Assemblies
- ASTM E2632/E2632M-13e1 Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Under-Deck Fire Test Response of Deck Materials
- ASTM E2707-09 Standard Test Method for Determining Fire Penetration of Exterior Wall Assemblies Using a Direct Flame Impingement Exposure
- ASTM E2726/E2726M-12a Standard Test Method for Evaluating the Fire-Test-Response of Deck Structures to Burning Brands
- ASTM E2748-12a Standard Guide for Fire-Resistance Experiments
- ASTM E2816-13a Standard Test Methods for Fire Resistive Metallic HVAC Duct Systems
- ASTM E2912-13 Standard Test Method for Fire Test of Non-Mechanical Fire Dampers Used in Vented Construction
- ASTM E535-12 Standard Practice for Preparation of Fire-Test-Response Standards
- ASTM E603-13 Standard Guide for Room Fire Experiments
- ASTM E605-93(2011) Standard Test Methods for Thickness and Density of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Material (SFRM) Applied to Structural Members
- ASTM E69-02(2007) Standard Test Method for Combustible Properties of Treated Wood by the Fire-Tube Apparatus
- ASTM E859-93(2011) Standard Test Method for Air Erosion of Sprayed Fire-Resistive Materials (SFRMs) Applied to Structural Members
- ASTM F1198-92(2012)e1 Standard Guide for Shipboard Fire Detection Systems
- ASTM F1534-10 Standard Test Method for Determining Changes in Fire-Test-Response Characteristics of Cushioning Materials After Water Leaching
- ASTM F1870-11 Standard Guide for Selection of Fire Test Methods for the Assessment of Upholstered Furnishings in Detention and Correctional Facilities
- ASTM F1989-05(2013) Standard Specification for Cooking Fire Suppression Blankets
- ASTM F1989-05(2013) Standard Specification for Cooking Fire Suppression Blankets
- ASTM F2058-07 Standard Specification for Candle Fire Safety Labeling
- ASTM G145-08 Standard Guide for Studying Fire Incidents in Oxygen Systems
- STP1163 Fire Standards in the International Marketplace
- STP1284 Fire Resistance of Industrial Fluids
- STP1427 Thermal Measurements: The Foundation of Fire Standards
- STP1427 Thermal Measurements: The Foundation of Fire Standards
- STP1517 Advances in the State of the Art of Fire Testing
- STP1541 Uncertainty in Fire Standards and What to Do About It
- STP344 Symposium on Fire Test Methods (1962)
- STP385 Moisture in Materials in Relation to Fire Tests
- STP406 Fire Resistance of Hydraulic Fluids
- STP422 Symposium on Fire Test Methods—Restraint & Smoke 1966
- STP464 Fire Test Performance
- STP464 Fire Test Performance
- STP502 Ignition, Heat Release, and Noncombustibility of Materials
- STP685 Design of Buildings for Fire Safety
- STP762 Fire Risk Assessment
- STP816 Behavior of Polymeric Materials in Fire
GOST
- GOST 12.1.004-91 Occupational safety standards system. Fire safety. General requirements
- GOST 12.1.018-93 Occupational safety standards system. Fire and explosion safety of static electricity. General requirements
- GOST 12.1.033-81 Occupaticnal safety standards system. Fire safety. Terms and defintions
- GOST 12.1.044-89 Occupational safety standards system. Fire and explosion hazard of substances and materials. Nomenclature of indices and methods of their determination
- GOST 12.1.114-82 Occupational safety standards system. Fire engineering. Symbolic representations
- GOST 12.3.046-91 Occupational safety standards system. Automatic fire fighting systems. General technical requirements
- GOST 14286-69 Wrenches for fire connecting equipment. Specifications
- GOST 15635-70 Refractory fire-clay products for hot-metal transier ladles lining. Specifications
- GOST 16363-98 Fire protective means for wood. Methods for determination of fire protective properties
- GOST 16714-71 Non-mechanized hand fire instruments. Specifications
- GOST 19297-2003 Treated for fire-resistance cotton fabrics. Specifications
- GOST 2071-69 Straps for fire-hoses
- GOST 23787.12-81 Solutions of biological fire retarding compound ПБC. Technical requirements, safety requirements and methods of analysis
- GOST 23787.7-79 Solutions of fire retarding preservative ПББ. Technical requirements, safety requirements and methods of analysis
- GOST 23790-79 Phosphates fire protective wood coating. Technical requirements
- GOST 23791-79 Phosphates fire protective still coating. Technical requirements
- GOST 23859.10-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Methods for the determination of titanium
- GOST 23859.1-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Method for the determination of copper
- GOST 23859.2-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Methods for the determination of silicon
- GOST 23859.3-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Methods for the determination of chromium
- GOST 23859.4-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Method for the determination of phosphorus
- GOST 23859.5-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Methods for the determination of iron
- GOST 23859.6-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Method for the determination of nickel
- GOST 23859.7-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Method for the determination of lead
- GOST 23859.8-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Methods for the determination of zirconium
- GOST 23859.9-79 Bronze fire-resistance. Method for the determination of cobalt
- GOST 24018.0-90 Nickel-based fire-resistant alloys. General requirements for methods of analysis
- GOST 24018.7-91 Nikel-based fire-resistant alloys. Methods for the determination of carbon
- GOST 24018.8-91 Nikel-based fire-ressistant alloys. Methods for the determination of sulphur
- GOST 25130-82 Intumescent fire protective wood coating. Technical requirements
- GOST 25131-82 Intumescent fire protective steel coating. Technical requirements
- GOST 25665-83 Phosphates fire protective steel coating of the mineral fibres. Technical requirements
- GOST 26342-84 Means of alarm, fire and alarm-fire systems. Types, basic parameters and dimensions
- GOST 27331-87 Fire engineering. Cassification of fires
- GOST 27483-87 Fire hazard testing. Test methods. Glow-wire test and guidance
- GOST 27484-87 Fire hazard testing. Test methods. Needle-flame test
- GOST 27924-88 Fire-hazard testing. Test methods. Bad-connection test with heaters
- GOST 27990-88 Means of alarm, fire and alarm-fire systems. General technical requirements
- GOST 28130-89 Fire engineering. Fire extinguishers, fire extinguishing systems and fire alarm systems. Grafical conventional signs
- GOST 31251-2008 Facades of buildings. Fire hazard test method
- GOST 30135-94 Fabricknitting carcasses for fire hoses. General specifications
- GOST 30247.0-94 Elements of building constructions. Fire-resistance test methods. General requirements
- GOST 30247.1-94 Elements of building constructions. Fire-resistance tests methods. Load-bearing and separating constructions
- GOST 30247.3-2002 Building structures. Fire-resistance tests methods. Elevator shaft doors
- GOST 30403-2012 Building structures. Fire hazard test method
- GOST 31251-2008 Facades of buildings. Fire hazard test method
- GOST 31565-2012 Cable products. Requirements of fire safety
- GOST 4.107-83 System of product quality indices. Fire-extinguishing powders. Nomenclature of indices
- GOST 4.188-85 Product-quality index system. Means for guarding, fire and guarding fire signalization. Nomenclature of indices
- GOST 4.331-85 Product-quality index system. Fire power pumps. Nomenclature of indices
- GOST 4.332-85 Product-quality index system. Fire extinguishing trucks. Nomenclature of indices
- GOST 4.407-85 Product-quality index system. Sporting, hunting and sport-hunting cartridges for rifled fire-arms. Index nomenclature
- GOST 4.445-86 Product-quality index system. Charging stations for fire extinguishers. Index nomenclature
- GOST 4.99-83 System of product quality indexes. Foaming agents for fire extinguishing. Nomenclature of indexes
- GOST 8556-72 Portable wood fire ladders
- GOST EN 13478-2012 Safety of machinery. Fire prevention and protection
- GOST EN 407-2012 Occupational safety standards system. Personal protective means of hands. Protective gloves from heat and fire. Technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST IEC 60331-12-2011 Tests for electric cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 12. Apparatus. Fire with shock at a temperature of at least 830 °C
- GOST IEC 60331-21-2011 Tests for electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 21. Procedures and requirements. Cables of rated voltage up to and including 0,6/1,0 kV
- GOST IEC 60331-23-2011 Tests for electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 23. Procedures and requirements. Electric data cables
- GOST IEC 60331-23-2011 Tests for electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 23. Procedures and requirements. Electric data cables
- GOST IEC 60331-25-2011 Tests for electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 25. Procedures and requirements. Optical fibre cables
- GOST IEC 60331-31-2011 Tests for electric cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 31. Procedures and requirements for fire with shock. Cables of rated voltage up to and including 0,6/1,0 kV
- GOST IEC 60332-1-1-2011 Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Part 1-1. Test for vertical flame propagation for a single insulated wire or cable. Apparatus
- GOST IEC 60332-1-2-2011 Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Part 1-2. Test for vertical flame propagation for a single insulated wire or cable. Procedure for 1 kW pre-mixed flame
- GOST IEC 60332-1-3-2011 Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Part 1-3. Test for vertical flame propagation for a single insulated wire or cable. Procedure for determination of flaming droplets/particles
- GOST IEC 60332-2-1-2011 Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Part 2-1. Test for vertical flame propagation for a single small insulated wire or cable. Apparatus
- GOST IEC 60332-2-2-2011 Tests on electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Рart 2 -2. Test for vertical flame propagation for a single small insulated wire or cable. Procedure for diffusion flame
- GOST IEC 60332-3-21-2011 Tests on electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Part 3-21. Flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched wires or cables. Category A F/R
- GOST IEC 60332-3-22-2011 Tests on electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Рart 3-22. Flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched wires or cables. Category A
- GOST IEC 60332-3-23-2011 Tests on electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Рart 3-23. Flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched wires or cables. Category B
- GOST IEC 60332-3-24-2011 Tests on electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Рart 3-24. Flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched wires or cables. Category C
- GOST IEC 60332-3-25-2011 Tests on electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Рart 3-25. Flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched wires or cables. Category D
- GOST IEC 60695-10-2-2013 Fire hazard testing. Part 10-2. Abnormal heat. Ball pressure test
- GOST IEC 60695-2-11-2013 Fire hazard testing. Part 2-11. Glowing/hot-wire based test methods. Glow-wire flammability test method for end-products
- GOST IEC 60695-2-13-2012 Fire hazard testing. Part 2-13. Glowing/hot-wire based test methods. Glow-wire ignition temperature (GWIT) test method for materials
- GOST R 12.2.144-2005 Occupational safety standards system. Fire-fighting technics. Safety requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 12.3.047-2012 Occupational safety standards system. Fire safety of technological processes. General requirements. Methods of control
- GOST R 12.3.047-2012 Occupational safety standards system. Fire safety of technological processes. General requirements. Methods of control
- GOST R 12.4.294-2013 Occupational safety standards system. Respiratory protective devices for selfrescue. Filtering devices with hood for escape from fire. Requirements, testing, marking
- GOST R 22.1.09-99 Safeti in emergencies. Monitoring and forecasing of forest fire. General requirements
- GOST R 41.34-2001 Uniform provisions concerning the type approval of vehicles with regard to the prevention of fire risks
- GOST R 50398-92 Fire hydraulic elevator. Specifications
- GOST R 50400-2011 Fire-fighting equipment. Hose branchings. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 50529-2010 Civil and service fire-arms, industrial and special devices. Safetу requirements and test methods for safetу
- GOST R 50530-2010 Cartridges for civil and service fire-arms, industrial and special devices. Safetу requirements and test methods for safetу
- GOST R 50571.17-2000 Electrical installations of buildings. Part 4. Protection for safety. Chapter 48. Choice of protective measures as a function of external influences. Section 482. Protection against fire
- GOST R 50588-2012 Foaming agents for fire extinguishing. General technical requirements and test methods
- GOST R 50862-2012 Safes, safe rooms and strong rooms. Requirements and methods of tests for resistance to burglary and fire
- GOST R 50969-96 Automatic gas fire extinguishing systems. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 50982-2009 Fire equipment. Specialized fires department tools. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51013-97 Nickel based fire-resistant, corrosion-resistant, precision alloys. Methods for titanium determination
- GOST R 51017-2009 Fire engineering. Wheeled fire extinguishers. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51043-2002 Аutomatic water and foam fire fighting systems. Sprinklers, spray nozzles and water mist nozzles. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51049-2008 Fire equipment. Pressure fire hoses. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51052-2002 Аutomatic water and foam fire extinguishing installations. Wet and dry systems alarm stations. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51057-2001 Fire fighting equipment. Portable fire extinguishers. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51072-2005 Protection doors. General technical requirements and test methods for resistance to burglary, bullet and fire
- GOST R 51091-97 Automatic dry chemical fire fighting systems. Types and dasic parameters
- GOST R 51115-97 Fire equipment. Fire turntable combined monitors. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51589-2000 Self-defence tubeless fire-arms (complex “OSA”). General technical requirements and test methods
- GOST R 51611-2000 Special purpose rounds for self-defense tubeless fire-arms (complex “OSA”). General technical requirements. Safety requirements and test methods
- GOST R 51737-2001 Automatic water and foam fire fighting systems. Sectional tubing couplings. General technical requirements. Methods of tests
- GOST R 51844-2009 Fire equipment. Fire-fighting cabinets. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 51879-2002 Fire-arms. Procedure of approval of proof marks of countries-members of International Permanent Commitee on testing small-arms
- GOST R 51888-2002 Civil and service gas-arms and fire-arms. Classification
- GOST R 51901.10-2009 Risk management. Fire risk management in enterprise
- GOST R 51928-2002 Nickel-based fire-resistant alloys. Methods for determination of boron
- GOST R 52283-2004 Fire-fighting centrifugal pumps. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 52284-2004 Fire aerial ladders. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 52316-2005 Fire equipment. Thermal equipment trips. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 52436-2005 Control equipment of intruder and intruder-fire alarm systems. Classification. General technical requirements and test methods
- GOST R 52625-2006 Lifts. Landing doors. Fire resistance test methods
- GOST R 52919-2008 Information technology. Physical security techniques. Classification and methods of tests for resistance to fire. Data rooms and data containers
- GOST R 53247-2009 Fire-fighting technics. Fire-engine vehicles. Classification, types and designations
- GOST R 53248-2009 Fire fighting technics. Fire fighting vehicles. Nomenclature of indices
- GOST R 53249-2009 Fire-fighting equipment. Sleeved watercollecting. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53250-2009 Fire-fighting equipment. Fire standpipe. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53251-2009 Fire-fighting equipment. Hand foam-nozzles. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53252-2009 Fire-fighting equipment. Foammixers. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53253-2009 Fire-fighting equipment. Suction gauzes. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53254-2009 Fire equipment. Ed fire ladders to be installed outside buildings. Buildings roof railings. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53255-2009 Fire equipment. Self-contained open-circuit compressed air breathing apparatus. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53256-2009 Fire equipment. Self-contained closed-circuit breathing apparatus with compressed oxygen. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53257-2009 Fire equipment. Full face masks breathing apparatus. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53258-2009 Fire equipment. The small size cylinders for apparatuses breathing and self-contained escape with compressed air. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53259-2009 Fire equipment. Self-contained escape with compressed air for protection of the people against toxic products at evacuation from smoking buildings from fire. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53260-2009 Fire equipment. Self-contained escape with chemical oxygen for protection of the people against toxic products at evacuation from smoking buildings from fire. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53261-2009 Fire equipment. Filter self-rescue for protection of people against toxic products at evacuation from smoking buildings from fire. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53262-2009 Fire equipment. Devices for control breathing apparatuses. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53263-2009 Fire equipment. Compressor unit for filling of low-volume ballons with compress air breathing apparatus for fireman. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53264-2009 Fire equipment. Special clothing for fire-fighter. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53265-2009 Mean of individual defence of feet for fire-fighter. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53266-2009 Fire equipment. Fire saving cord. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53267-2009 Fire equipment. Fire snap hook. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53268-2009 Fire equipment. Fire safety belt. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53269-2009 Fire equipment. Helmets for firefighters. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53270-2009 Fire equipment. Fire lantern. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53271-2009 Fire equipment. Fire escape chute. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53272-2009 Fire equipment. Fire rope descenders. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53273-2009 Fire equipment. Fire jumping down rescue devices. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53274-2009 Fire equipment. Fire rescue chute. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53275-2009 Fire equipment. Fire departament hand-operated ladders. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53276-2009 Fire equipment. Hanging ladders for rescue from height. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53277-2009 Fire equipment. Equipment for maintenance of fire hoses. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53278-2009 Fire equipment. Fire valves. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53279-2009 Fire equipment. Fire connecting heads. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53280.1-2010 Automatic fire extinguishing systems. Fire extinguishing media. Part 1. Foam fire extinguishing concentrates for surface application to water – miscible liquids. General technical requirements and test methods
- GOST R 53280.2-2010 Automatic fire extinguishing systems. Fire extinguishing media. Part 2. Foams concentrate for subsurface extinguishing of fires oil and petroleum tanks. General technical requirements and test methods
- GOST R 53280.3-2009 Automatic fire extinguishing systems. Fire extinguishing media. Part 3. Gaseous extinguishing media. Test methods
- GOST R 53280.4-2009 Automatic fire extinguishing systems. Extinguishing medium. Part 4. Dry fire extinguishing powders. General technical requirements and test methods
- GOST R 53280.5-2009 Automatic fire extinguishing systems. Extinguishing medium. Part 5. Special dry fire extinguishing powders. Classification, general technical requirements.Test methods
- GOST R 53281-2009 Automatic gas fire extinguishing systems. Cylinders and cylinder banks. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53282-2009 Automatic gas fire extinguishing systems. Isothermal tanks. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53283-2009 Automatic gas fire extinguishing systems. Distributing valves. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53284-2009 Fire engineering. Generators of extinguishing aerosol. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53285-2009 Fire engineering. Portable generators of extinguishing aerosol. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53286-2009 Fire engineering. Automatic dry chemical fire fighting system. Module. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53287-2009 Water and foam fire fighting systems. Fire alarm hydraulic, fire foam inducer, feeder. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53288-2009 Automatic water and foam extinguishers systems. Automatic fire water mist spray extinguishers systems. Modules. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53289-2009 Ceiling type water sprinklers (concealed, flush and recessed). Fire sensitivity test
- GOST R 53290-2009 Fire engineering. Foam fire-extinguishing installations. Low expansion foam generators for subsurfase extinguishing in tanks. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53291-2009 Portable and movable devices of fire extinguishing with high-velosity submission of fire quenching matter. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53292-2009 Fire retardant compositions and substances for wood. General requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53293-2009 Fire hazard of substances and materials. Materials, substance and fire protective means. Identification by thermal analysis methods
- GOST R 53295-2009 Fire retardant compositions for steel constructions. General requirement. Method for determining fire retardant efficiency
- GOST R 53296-2009 Fire fighting lifts placing. Requirements of fire safety
- GOST R 53298-2009 Suspended ceilings. Fire resistance test method
- GOST R 53299-2009 The test method for the fire resistance. Ventilation ducts
- GOST R 53299-2013 Ventilation ducts. The test method for the fire resistance
- GOST R 53301-2009 Fire dampers of ventilation systems. The test method for the fire resistance
- GOST R 53301-2013 Fire dampers of ventilation systems. The test method for the fire resistance
- GOST R 53302-2009 The equipment of smoke control systems. The test method for the fire resistance
- GOST R 53303-2009 Building constructions. Fire doors and gates. Test methods for smoke-and-gas leakage
- GOST R 53304-2009 Trunks of refuse chutes. The test method on fire resistance
- GOST R 53305-2009 Smoke shields. The test method for the fire resistance
- GOST R 53306-2009 Enclosing building structures crossing junction points by using pipe, which is made of polymeric materials. Fire resistance test
- GOST R 53307-2009 Elements of building constructions. Fire doors and gates. Fire resistance test method
- GOST R 53309-2009 Buildings and building’s fragments. Method of real fire tests. General requirements
- GOST R 53310-2009 Through penetration for cables, hermetic inputs and through penetration of electric current types. Requirements of fire safety. Fire resistance test methods
- GOST R 53311-2009 Coatings cables fire retardant. Methods for determination of fireproof efficiency
- GOST R 53313-2009 Electrical mounting appliances. Requirements of fire safety. Test methods
- GOST R 53316-2009 Cable lines. Circuit integrity under fire. Test method
- GOST R 53321-2009 Thermal devices on various kind of fuel. Fire safety requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53324-2009 Dyking of storage tanks. Fire safety requirements
- GOST R 53325-2012 Fire techniques. Means of fire automatics. The general technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53326-2009 Fire equipment. Self-contained open-circuit compressed air breathing apparatus. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53328-2009 Fire fighting technics. Fire extingushing trucks. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53329-2009 Fire elevators. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 53331-2009 Fire-fighting equipment. Hand nozzles. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53332-2009 Fire equipment. Fire motor pumps. Main parameters. General technical requirements. Methods of testing
- GOST R 53961-2010 Fire-fighting equipment. Underground fire hydrants. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 54019-2010 Fire hazard testing. Part 2-20. Glowing/hot-wire based test methods. Hot-wire coil ignitability. Apparatus, test method and guidance
- GOST R 54081-2010 Influence of environmental conditions appearing in nature on the technical products. Overall performance. Fire
- GOST R 54103-2010 Fire hazard testing. Test methods. Glow-wire test and guidance
- GOST R 54344-2011 Fire equipment. Mobile manipulation vehicle systems for eliminating of emergencies and fire extinguishing. Classification. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 54495-2011 Glass and glass products. Fire resistance test method
- GOST R 55149-2012 Fire techniques. Individual fire alarm devices. The general technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 55183-2012 Passenger cars on locomotive traction. Fire safety requirements
- GOST R 55230-2012 Marine, locomotive and industrial engines. Fire protection requirements
- GOST R 55895-2013 Fire equipment. Robotics control systems for eliminating of emergencies and fire extinguishing. General technical requirements. Test methods
- GOST R 55896-2013 Building structures. Doors the enclosures of lift shaft. Fire resistance test method
- GOST R IEC 60331-11-2012 Tests for electric and optical cables under fire conditions. Circuit integrity. Part 11. Apparatus. Fire alone at a flame temperature of at least 750 °C
- GOST R IEC 60332-3-10-2011 Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions. Part 3-10. Flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched wires or cables. Apparatus
- GOST R IEC 60695-10-2-2010 Fire hazard testing. Part 10-2. Abnormal heat. Ball pressure test
- GOST R IEC 60695-1-1-2003 Fire hazard testing. Part 1-1. Guidance for assessing the fire hazard of electrotechnical products. General guidelines
- GOST R IEC 60695-2-10-2011 Fire hazard testing. Part 2-10. Glowing/hot-wire based test methods. Glow-wire apparatus and common test procedures
- GOST R IEC 60695-2-11-2010 Fire hazard testing. Part 2-11. Glowing/hot-wire based test methods. Glow-wire flammability test method for end-products
- GOST R IEC 60695-2-2-2011 Fire hazard testing. Part 2. Test methods. Section 2. Needle-flame test
- GOST R ISO 3935-2005 Shipbuilding. Inland navigation. Fire-fighting water system. Pressures
- GOST R ISO 5797-2010 Ships and marine technology. Windows and side scuttles for fire-resistant constructions
- GOST R ISO 6942-2007 Occupational safety standards system. Clothing for protection against heat and fire. Assessment methods of materials and material assemblies when exposed to а source of radiant heat
CISCA
천장 및 인테리어 시스템 건설 협회 (CISCA)는 음향 및 특수 천장과 내부 마감재 업계의 협회로써 실내인테리어 건설 산업의 발전을 위해 1950 년에 설립 된 국제 무역 협회입니다.(http://www.cisca.org/i4a/pages/index.cfm?pageid=1)
CISCA의 임무는 회원 간의 통신을위한 양질의 교육, 자원 및 포럼을 제공하는 것이며, CISCA 회원은 전세계 주요 업체, 유통 업체, 제조 업체 및 독립적 인 제조 업체 대표자 600 여명으로 구성되어 있습니다.
CISCA의 핵심 목적
CISCA는 천정 및 인테리어 시스템 건설 산업의 상호 발전 및 번영을 목적으로 하고 있습니다.
CISCA의 기술 자료
CISCA는 2007 Procedure 등 관련 기술적 자료를 제공합니다.
일부 관련 시험은 PSB test와 연관이 있습니다.
CISCA Procedures
CISCA 절차 단원 5 축하중 시험
Section 5
Pedestal Axial Load Test
Purpose:
To verify the axial load an access floor pedestal assembly can withstand without structural failure or damage to components inclusive of threads, nuts, collars, etc.
Preparation:
1.A minimum of three (3) randomly selected pedestal assemblies shall be tested for each floor height. Pedestals shall be identical to those used in normal installations for their corresponding floor heights, including thread engagements normally utilized in field conditions.
2.Pedestal assemblies shall be tested for maximum floor heights of each assembly design or configuration.
3.Loads shall be imposed and measured through a properly calibrated and appropriately sized load sensor over the center of the pedestal head. The load indentor or applicator may be machined to integrate with the pedestal head to simulate the loading of the four corners of the panels.
Test Procedure:
1.Align the Pedestal assembly in the testing apparatus and apply an increasing load centered on the pedestal until the desired load is reached. Hold imposed load for minimum of one (1) minute duration. The load shall then be relaxed and the assembly visually inspected for damage. Adjusting devices, locking devices, threads shall be workable by hand. Rate of load application shall not exceed 10,000 pounds per minute (44.5 kN/min).
Report:
1.Reference of testing procedure described herein by CISCA A/F section number shall be included in report.
2.All apparatus, equipment, instrumentation, accuracy ranges, etc. shall be described including equipment calibration/certification dates.
3.Materials tested shall be fully described or referenced to manufacturers’ drawings and part numbers containing the following:
- Materials of construction, weight, nominal dimensions and thicknesses.
4. Report load applied and relaxed for each pedestal and describe damage to components, if any.
Section 10
Air Leakage Test
(Through Panel Seams)
Purpose:
To determine the rate at which air will pass through the cracks and gaps in an access floor panel assembly, at
a specified and controlled differential static air pressure. This test applies only to floors used for underfloor air distribution.
Preparation:
1.The test shall be performed on a specimen of panels in a relatively airtight box or chamber, as shown below. The gap between the perimeter of the floor panels and the chamber opening shall be sealed to minimize air leakage.
2.The dimensions of the panel assembly shall be at least 72 inches (1829 mm) square. Finished floor height shall be 12 inches (305 mm), or the maximum height of the system; whichever is less.
3.Any coatings, stringers, gaskets, pads, clips, fasteners, or other materials normally used shall be
identical to that utilized in an installed system. The pedestals shall be anchored to the base of the chamber only if such anchorage will affect the air leakage rate in some way. If so, such anchorage
shall be described in the report.
4.A controllable blower, fan, or air pump shall be fitted to the chamber to supply airflow to the chamber at
a rate sufficient to maintain the positive air pressure required. The system should provide essentially constant airflow for a period of time sufficient to obtain readings of airflow rate and pressure.
5.A flowmeter or other suitable device to measure the rate of airflow into the test chamber shall be fitted.
A manometer or other suitable device to measure the differential test pressures shall be connected between the chamber and atmosphere.
Note: The referenced test method, ASTM E283, requires the device be capable of recording the pressure within ±2% of set point. The static air pressure differentials typically employed in under floor air
distribution systems are much lower than in the referenced method, so care must be taken by the test agency to employ the appropriate pressure measuring device.
Test Procedure:
1.Calibrate the air leakage test equipment in accordance with the calibration instructions in ASTM E283 Standard Test Method For Determining Rate of Air Leakage Through Exterior Windows, Curtain Walls, and Doors Under Specified Pressure Differences Across the Specimen , except that the calibration pressure shall be 0.10 inch of water column (25 Pa).
2.With the floor specimen installed as described above, adjust the total airflow into the chamber to provide the specified test pressure difference across the test specimen. When the test conditions have stabilized, record the airflow through the flowmeter, and the test pressure difference. This measured air flow is designated the total air flow, Qt(p)n, where p is the pressure, and n is the number of the measurement. Measure the barometric pressure, B, and temperature of the air at the test specimen, T.
3.Repeat the measurement of the leakage at each pressure level at least 4 times. Calculate the arithmetic average of all leakage measurements at each pressure, Qt(p).
4.Seal all gaps and holes in the floor specimen.
5.With the floor specimen sealed, measure the amount of air leakage through the test chamber itself, at the same air pressure differentials as in step 2. Each measured air flow is designated the extraneous airflow, Qe(p)n.
6.Repeat the measurement of the extraneous leakage at each pressure the same number of times as in step 3. Calculate the arithmetic average of all extraneous leakage measurements at each pressure, Qe(p).
7.Measure the total crack length between the access floor panels, l. Do not include any of the joints between the perimeter of the specimen and the chamber.
The Calculation:
1.Calculate ratio Ap/lp , where:
Ap = Area of a floor panel, ft² (m²)
lp = Perimeter of a single floor panel, ft² (m²)
Note: For some systems, where multiple panel sizes or shapes are employed together in one floor assembly, determination of lp may require more careful analysis. Generally, the perimeter of each panel should be measured only once in determining lp.
1.Express the total average air flow at each pressure Qt(p), and the extraneous average air flow at each pressure Qe(p), in terms of flow at standard conditions, as outlined in ASTM E283.
Note: Ensure all units of measure referenced in the E283 calculation are observed, and that the correct equation is employed.
1.Express the air leakage through the test specimen at each pressure, Qs(p), as
Qs(p) = Qt(p) – Qe(p), ft³/min (L/s) (1)
1.Calculate the rate of air leakage per unit crack length at each pressure, ql(p), as
ql(p) = Qs(p)/l, ft³/min-ft (L/s-m) (2)
1.Calculate the rate of air leakage per unit area at each pressure, qA(p), as
qA(p) = ql(p) / [2 (Ap/lp)], ft³/min-ft² (L/s-m²) (3)
Report:
1.Reference of testing procedure described herein by CISCA A/F section number shall be included in the report.
2.All apparatus, equipment, instrumentation, accuracy ranges, etc., shall be described including equipment calibration/certification dates.
3.Materials tested, and specimen configuration(s) should be fully described in text and/or photograph and/or drawing, or by reference to manufacturer’s drawings and/or part numbers, including the following:
Panels:
. Floor finishes
. Materials of panel construction
. Weight, nominal dimensions and thicknesses
Supporting structure:
. Height
. Materials, sections, fasteners, adhesives or other anchors
Other:
. Fully describe other materials used in the mock-up
4. For each of test pressures, report the rate of air leakage per unit crack length, and per unit area, as noted. At a minimum, report the air leakage rate at the pressures noted in the table. Other pressures may also be reported, at the discretion of the proponent or authority. Calculated accuracy of the measured air leakage, based on the precision of the air pressure measurement.
CISCA Glossary of Terms
Access Floor System
An access floor system is an elevated or “raised” floor area upon another floor (typically a concrete slab in a building) creating an interstitial space for service distribution. It consists of modular floor panels that are designed to be removable from their support so that “access” to services is quickly and easily achieved. These services may include but are not limited to electric power, data, plumbing, telecom, environmental control, air conditioning, fire detection suppression, security, etc.
Air Leakage
As it pertains at access floors, air leakage is defined as the passage of air from an underfloor air cavity through elements other than the designed air outlet devices. Leakage typically falls into two categories: 1) leakage in the air cavity under the floor due to construction quality, and 2) leakage through floor panel seams and other non-air outlet devices.
Axial Load
A vertical load (or force) whose line of action passes through the center of the member’s cross sectional area and is perpendicular to the plane of the section such that no bending or torsion moments are produced. This is the load that is typically specified when referring to the axial load performance of an access floor pedestal support.
Beam Deformation
Deformation is defined as the act of distorting or changing the shape or dimensions of a structural element or body resulting from forces or stresses. Beam deformation as related to access floors is generally the term used when referring to the permanent set of the entire span of the access floor panel after application of a rolling load and is determined by measuring the overall flatness of the access floor panel before and after the application of the load.
Concentrated Load
A single load or force that has a small contact area as to be negligible compared with the entire surface area of the supporting member. Concentrated loads (sometimes referred to as static loads) are typically imposed by stationary furniture and equipment with legs. A concentrated load is applied to the surface of the panel (1″x 1″ square or 1.128″ diameter indentor) (25.4 mm x 25.4 mm square or 28.65 mm diameter) resulting in deflection and permanent set. Concentrated load rating is specified in pounds force applied over a one square inch (645 mm2) area.
Deflection
Deflection is the vertical displacement of a structural member or system under load. This is generally referred to when discussing the vertical displacement a floor panel experiences upon application of a concentrated load or uniform load.
Design Load
The load expected to be imposed on the floor system in service. The access floor concentrated load rating is not the safe working load or design load for the floor system.
Dynamic Load
Loads that vary significantly with time as measurements are being made. Two dynamic loads are generally referred to: rolling loads and impact loads.
Finished Floor Height
Finished floor height is defined as the height of the access floor system as measured from the top of the supporting sub-floor to the top of the access floor panel.
Impact Load
Impact loads are caused by objects being accidentally dropped onto an access floor. These loads are defined by the weight of the load, height, or distance dropped, impact area, and hardness/softness of the object. Impact loads generate severe shocks that can cause structural and panel damage. Impact loads most often occur during construction, move-in, and equipment/furniture rearrangements.
Live Load
A live load is produced by the use or occupancy of the building. This does not include construction, environmental, seismic, or access floor dead loads. The live load should not be confused with the uniform load capacity of an access floor.
Local Deformation
Local deformation is generally the term used when referring to the permanent set recorded along the wheel path after a rolling load test. It is determined by measuring the local flatness of the panel along the wheel path before and after the application of the load using a 6″ (152 mm) spanner perpendicular to the wheel path. The difference between before and after measurements is defined as local deformation.
Overturning Moment
Overturning moment is the term generally used to refer to the capacity of the floor pedestal attached to a supporting floor to withstand tip over forces generated by the application of a lateral force applied to the top of a moment arm. Overturning moment capacity is calculated by multiplying the lateral force by the height at which the force is applied.
Panel/Panel Assembly
Modular and removable structural floor element or elements designed to rest on separate or integral elevated supports that may be used as an interstitial space for distribution of building services (wire, cable, air, etc.).
Pedestal (Adjustable Height)
An access floor pedestal with adjustable height option is defined as the structural element that supports the access floor panel and raises it off the floor slab to create an interstitial space for service distribution. The adjustable height or leveling feature of the pedestal allows the access floor panels to be installed level regardless the changes in elevation of the floor slab.
Pedestal (Fixed Height)
A fixed height floor pedestal is defined as the structural element that supports the access floor panel and raises it off the slab to create an interstitial space for service distribution. The fixed height floor pedestals and corresponding access floor panels are designed to lay on the floor slab and follow its contour and undulations.
Permanent Set
A material that is deflected so far that its elastic properties have been exceeded and it does not return to its original condition upon release of load is said to have taken a “permanent set.”
Raised Floor System (See Access Floor System)
Rolling Load
Rolling loads are dynamic loads typically imposed by equipment on wheels moving across the access floor.
Stanchion
The term stanchion is sometimes used to describe an access floor pedestal.
Static Load
Static load is defined as a force that does not undergo a change in magnitude or direction during a measurement procedure. Three static loads are generally referred to: concentrated, ultimate and uniform loads.
Stringer
A stringer is a structural element used to connect access floor pedestals together, thus providing lateral stability to the system and floor supports.
Uniform Load
Uniform load is a static force applied equally over the entire area of an access panel and is typically imposed by stationary furniture, equipment without legs, boxes, pallets, etc. The uniform load rating is specified in pounds per square foot or Newtons per square meter.
Ultimate Load
The greatest applied vertical static force(s) beyond which additional deflection is achieved without additional load or resistance.