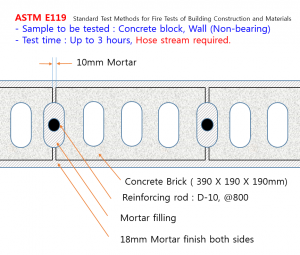
아래 각 시험규격은 저희 해외 파터너 시험소에서 수행할 수 있습니다.
해외특송 안내 당일 해외특송서비스의 경우, 보통 2일 후 현지 시험소에 시료가 도착합니다.
1. Altitude
ASTM D4169-14;
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006:
Chapter 3-09 Test CL9 – Rapid and Explosive Decompression;
GR-63-CORE, Issue 1 Paragraph 4.1 and 5.1;
GR-63-CORE, Issue 2, 3 Paragraph 4.1.3 and 5.1.3;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 . Low air pressure;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 . Low air pressure;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 . Low air pressure;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 . Low air pressure;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 . Low air pressure;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IEC 60721-3-2;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev.3 Test Number 3;
ISO 10236 Part 9;
ISO 14708-1:2000(E);
MIL-B-49430C (ER) Paragraph 4.8.7;
MIL-B-49458C (ER) Paragraph 4.7.7;
MIL-PRF-49471B (CR) Paragraph 4.7.7;
MIL-STD-202F Method 105C, Conditions A, B, C, and F;
MIL-STD-202G Method 105C, Conditions A, B, C, and F;
MIL-STD-810C Method 500.1, Procedures I and II;
MIL-STD-810D Method 500.2, Procedures I and II;
MIL-STD-810E Method 500.3, Procedures I and II;
MIL-STD-810F Method 500.4, Procedures I and II;
MIL-STD-810G Method 500.5 Procedures I, II, and III;
RTCA DO-160D, E, F, G Section 4, Paragraph 4.6.1, Category Ax, Bx, Cx, Dx, Ex, Fx;
UN Transport of Dangerous Goods, Test T.1
2. Temperature/Altitude
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006:
Chapter 3-11 Test CL11 – High Temperature – Low Pressure,
Chapter 3-12 Test CL12 – Low Temperature – Low Pressure Test,
Chapter 3-13 Test CL13 – Low Temperature – Low Pressure – High Humidity;
MIL-STD-810C Method 504.1, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810D Method 520.0, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810E Method 520.1, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810F Method 520.2, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810G Method 520.3, Procedure I;
RTCA DO-160D, E, G Section 4
3. Bench Handling
MIL-STD-810C Method 516.2, Procedure V;
MIL-STD-810D Method 516.3, Procedure VI;
MIL-STD-810E Method 516.4, Procedure VI;
MIL-STD-810F Method 516.5, Procedure VI;
MIL-STD-810G Method 516.6, Procedure VI
4. Bounce (Loose Cargo Vibration)
ASTM D999, D999-96 (Method A2), D4169-14;
IEC 68-2-55, IEC 60068-2-55, Test Ee;
ISTA 1A-2014, ISTA 2A-2011, ISTA 3A-2008;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev.2 Test Number 4;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure IX Part 2, X, and XI;
MIL-STD-810D Method 514.3, Category 3, Procedure II;
MIL-STD-810E Method 514.4, Category 3, Procedure III;
MIL-STD-810F Method 514.5, Category 5, Procedure II;
MIL-STD-810G Method 514.6 Category 5, Procedure II
5. Compression, Stacking
ASTM D642, D4169, D7386-12;
GR-63 Core;
ISTA 2A-2011
6. Drop & Topple
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006;
ETSI EN 300 019-2-77:2003-04;
IEC 68-2-31, IEC 60068-2-31, Test Ec;
IEC 68-2-31, IEC 60068-2-31 amm-1982: Test Ec;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Drop and Topple;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1: 03 – Drop and Topple;
ISTA 2A-2011;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 26;
QM-333 Paragraph 13.0, Categories A, B, C, D
7. Drop Test
ASTM D1083, D1083-91 Paragraph 10, 11, 12, 13;
ASTM 5276, ASTM 5276-98; ASTM D7386-12
EN 50130 Section 21 Free Fall (Operational);
EN 50130:1999 Section 21 Free Fall (Operational);
GR-63-CORE, Paragraph 5.3.1, Category A & B;
GR-63-CORE, Paragraph 5.3.2;
IEC 68-2-32, IEC 60068-2-32: Test Ed, Free Fall;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IEC 60721-3-2;
MIL-B-49430C (ER), Paragraph 4.8.3;
MIL-PRF-49471B (CR), Paragraph 3.10;
MIL-STD-810C Method 516.2 Procedure II;
MIL-STD-810D Method 516.3 Procedures III and IV;
MIL-STD-810E Method 516.4 Procedures III and IV;
MIL-STD-810F Method 516.5 Procedure IV;
MIL-STD-810G Method 516.6 Procedure IV;
MIL-STD-1344A Method 2015;
ISO 10651-3 Lung Ventilators Medical Use Part 3 Section 4: Protection against mechanical hazards;
BMW Group GS95003-1;
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5: Environmental Test Methods DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006;
ISTA 1A-2014;
ISTA 2A-2011;
ISTA 3A-2008;
ASTM D4169-14;
IS 10236 Part 15;
ISO 14708-1:2000(E)
8. Fire, Flammability
GR-63 Core;
RTCA/DO-160E, F, G Section 26;
UL-94
9. Immersion
IEC 60529, Temporary Immersion IPx7, IPx8;
IEC 60529-2001 COR 1 2003, Temporary Immersion IPx7 Paragraph 14.2.7;
IEC 60529-2001 COR 1 2003, Continuous Immersion IPx8 Paragraph 14.2.8;
ISO 20653 Degrees of protection (IP-Code);
ISO 20653: 2006 Degrees of protection (IP-Code), IPx7, IPx8;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 19;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-STD-810C Method 512.1, Procedure I and IV;
MIL-STD-810D Method 512.2, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810E Method 512.3, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810F Method 512.4, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810G Method 512.6, Procedure I
10. Mechanical Shock
ASTM D4169-14, Schedule J- Concentrated Impact (Test Method D6344);
BMW Group GS95003-1;
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5: Environmental Test Methods;
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006;
ETSI 300-019-2-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8;
GM 9123P;
IEC 68-2-27, IEC 60068-2-27:Test Ea;
IEC 68-2-29, IEC 60068-2-29:Test Eb;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Shock;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Shock;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Shock;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Shock;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Shock;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IEC 60068-2-75 – Hammer Tests;
IEC 62262 (EN 62262, IK ratings) – Impact;
IS 10236 Part 10 – Bump, IS 10236 Part 12 – Shock;
ISO 10651-3 Lung Ventilators Medical Use Part 3 Section 4: Protection against
mechanical hazards;
ISTA 1A-2014, ISTA 2A-2011, ISTA 3A-2008;
JEDEC Standard JESD22-B104C;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 4, 24;
MIL-B-49430, Paragraph 4.8.5;
MIL-B-49458C (ER), Paragraph 4.7.5;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-PRF-49471B (CR), Paragraph 3.9;
MIL-STD-202F Method 213B, Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G,H, I, J, and K;
MIL-STD-202G Method 213B, Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G,H, I, J, and K;
MIL-STD-810C Method 516.2, Procedures I, III, IV, and VI;
MIL-STD-810D Method 516.3, Procedures I, II, V, and VIII,
MIL-STD-810E Method 516.4, Procedures I, II, V, and VIII;
MIL-STD-810F Method 516.5, Procedures I, II, III, V, and VIII;
MIL-STD-810G Method 516.6 Procedures I, II, III, V, and VIII;
MIL-STD-883A Method 2002.1, Condition A;
MIL-STD-883E Method 2002.3, Condition A;
MIL-STD-883F Method 2002.4, Condition A;
MIL-STD-883G Method 2002.5, Condition A;
MIL-STD-883H Method 2002.6, Condition A;
MIL-STD-883J Method 2002.7, Condition A;
MIL-STD-1344A Method 2004.1, Conditions A, B, C, E, F, G, H, and I;
MIL-STD-1344A Method 2004.1, Conditions A, B, C, E, F, G, H and I;
RTCA DO-160D, 160E Section 7, Paragraphs 7.2.1, 7.2.2, Operational;
RTCA DO-160D Section 7, Paragraphs 7.3.1, 7.3.1.1, Crash Safety;
RTCA DO-160E, 160F, 160G Section 7, Paragraphs 7.3.1, 7.3.2, Crash Safety;
UL-1642 4ED Rev August 2006, Paragraph 14A
11. Rain (Water Test)
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5: Environmental Test Methods
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006 Chapter 3-27;
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006 Chapter 3-28;
IEC 68-2-18, IEC 60068-2-18 Test Rb2;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Rain;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Rain;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Rain;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Rain;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Rain;
IEC 60529-2001 -02, Protection Against Water;
IEC 60529 IPX1 Vertically Dripping;
IEC 60529 IPX2 Dripping (150 tilted);
IEC 60529 IPX3 Spraying;
IEC 60529 IPX4 Splashing;
IEC 60529 IPX5 Jetting;
IEC 60529 IPX6 Powerful Jetting;
IEC 60529 IPX7 Immersion;
IEC 60529 IPX8 Immersion;
IEC 60529 IPX9 Resist Ingress of High Temperature (Steam)/High Pressure Water;
IS 10236 Part 14 – Driving Rain;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev.2 Test Number 11,12,16;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-STD-810C Method 506.2, Procedures I and II;
MIL-STD-810D Method 506.3, Procedures I and II;
MIL-STD-810E Method 506.4, Procedures I and III;
MIL-STD-810F Method 506.5, Procedures I and III;
MIL-STD-810G Method 506.6, Procedures I and III;
MIL-STD-108, Splashproof;
MIL-STD-108E, Splashproof Paragraph 4.9;
RTCA DO-160D,E,F,G Section 10;
MIL-STD-108, Splashproof;
MIL-STD-108E, Splashproof Paragraph 4.9;
RTCA DO-160D,E,F,G Section 10;
12. Contamination by Fluids
MIL-STD-108, Splashproof;
MIL-STD-108E, Splashproof Paragraph 4.9;
RTCA DO-160D,E,F,G Section 10;
13. Explosive Atmosphere Method 511 Section 9 Explosive proofness Test
MIL-STD 810B:67Method 511;
MIL-STD 810C:75Method 511;
MIL-STD 810D:83Method 511;
MIL-STD 810E:89 Method 511;
MIL-STD 810F:00 Method 511;
MIL-STD 810G:08 Method 511;
RTCA/ DO-160C Section 9;
RTCA/DO-160D:97+CHG1:00+ CHG2:01+ CHG3:02 Section 9;
RTCA/DO-160E:04 Section 9;
RTCA/DO-160F:07 Section 9;
RTCA/DO-160G:10 Section 9
14. Icing
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006 Chapter 4-04 Test CN4;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev.2 Test Number 18;
MIL-STD 810 D,E,F,G Method 521;
RTCA/DO-160 C, D, E, F,G Section 24
15. Warehouse Stacking and Vehicle Stacking (Compression)
ASTM D4169-14;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Static Load;
ISTA 2A-2011
16. Salt Fog (Spray)
ASTM B117, B117-97, B117-2003;
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5: Environmental Test Methods;
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006 Chapter 4-02 Test CN2;
DET NORSKE VERITAS (DNV) STANDARD FOR CERTIFICATION NO. 2.4 : ENVIRONMENTAL TEST SPECIFICATIONFOR INSTRUMENTATION AND AUTOMATION EQUIPMENT (April 2006);
GM 9123P;
GMW 14872;
IEC 68-2-11, Test Ka, Salt Fog, Corrigendum 1999;
IEC 68-2-52, IEC 60068-5-52, Test Kb Salt Fog, Cyclic;
IS 10236 Part 6;
ISO 9227;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 9;
MIL-C-83733;
MIL-C-5541E Class: 1A and 3;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-STD-202F Method 101D, Conditions A and B;
MIL-STD-202G Method 101E, Conditions A and B;
MIL-STD-810C Method 509.1;
MIL-STD-810D Method 509.2;
MIL-STD-810E Method 509.3;
MIL-STD-810F Method 509.4;
MIL-STD-810G Method 509.5;
MIL-STD-883E Method 1009.8, Conditions A, B, C and F;
MIL-STD-883F Method 1009.8, Conditions A, B, C and F;
MIL-STD-883G Method 1009.8, Condition A, B, C and F;
MIL-STD-883H Method 1009.8, Condition A, B, C and F;
MIL-STD-883J Method 1009.8, Condition A, B, C and F;
MIL-STD-1344A Method 1001.1, Conditions A, B, C and D;
RTCA DO-160D, E, F, G Section 14
17. Temperature
ASTM D4169-14;
“BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5: Environmental Test Methods;
Chapter 3-14 Test CL14 – Thermal Shock and Rapid Rate of Change of
Temperature;”
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006;
“DET NORSKE VERITAS (DNV) STANDARD FOR CERTIFICATION NO. 2.4:
ENVIRONMENTAL TEST SPECIFICATIONFOR INSTRUMENTATION
ANDAUTOMATION EQUIPMENT (April 2006);”
EIA/JEDEC Standard EIA/JESD22-A104-B;
EN 50130-5 Section 8 Dry Heat (Operational);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 8 Dry Heat (Operational);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 9 Dry Heat (Endurance);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 10 Cold (Operational);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 11 Temperature Change (Operational);
ETSI 300-019-2-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8;
GM 9123P;
GR-63-CORE, Paragraph 5.1.1.1, Low Temperature;
GR-63-CORE, Paragraph 5.1.1.2, High Temperature;
GR-1221-CORE, Paragraph 6.2.4, High Temperature;
GR-1221-CORE, Paragraph 6.2.6, Low Temperature;
GR-1221-CORE, Paragraph 6.2.7, Thermal Shock;
IEC 68-2-1, IEC 60068-2-1, Test Aa, Ab, Ac, and Ad, Low Temperature;
IEC 68-2-2, IEC 60068-2-2, Test Ba, Bb, Bc and Bd, High Temperature;
IEC 68-2-14, IEC 60068-2-14, Test Na, Nb and Nc, Temperature Cycling;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Low Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – High Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Temperature cycle;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Low Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – High Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Temperature cycle;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Low Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – High Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Temperature cycle;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Low Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – High Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Temperature cycle;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Low Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – High Temperature;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Temperature cycle;
IEC 60721-3-2;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IS 10236 Part 2 – Dry Heat;
IS10236 Part 3 – Cold;
IS 10236 Part 8 – Thermal Shock;
ISO 14708-1:200 (E);
ISTA 1A-2014, ISTA 2A-2011, ISTA 3A-2008;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 13, 20, 22;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-STD-202F Method 107D, Conditions A, A-1, A-2, A-3, B, B-1, B-2, B-3, F, F-1, F-2, and F-3, Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-202G Method 107G, Conditions A, A-1, A-2, A-3, B, B-1, B-2, B-3, F, F-1, F-2, and F-3, Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-202F, G Method 108A, High Temperature;
MIL-STD-810C Method 501.1, Procedure I, High Temperature;
MIL-STD-810C Method 501.1, Procedure II, Temperature Cycling;
MIL-STD-810C Method 502.1, Procedure I, II, III Low Temperature;
MIL-STD-810C Method 503.1, Procedure I, Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-810D Method 501.2, Procedure I, II High Temperature;
MIL-STD-810D Method 502.2, Procedure I, II, III Low Temperature;
MIL-STD-810D Method 503.2, Procedure I, Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-810E Method 501.3, Procedure I, II High Temperature;
MIL-STD-810E Method 502.3, Procedure I, II Low Temperature;
MIL-STD-810E Method 502.3, Procedure III, Low Temperature;
MIL-STD-810E Method 503.3, Procedure I, Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-810F Method 501.4, Procedure I, II High Temperature;
MIL-STD-810F Method 502.4, Procedure I, II, III Low Temperature;
MIL-STD-810F Method 503.4, Procedure I, II Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-810G Method 503.5, Procedure I, II Thermal Shock;
MIL-STD-810G Method 501.5, Procedure I, II High Temperature;
MIL-STD-810G Method 502.5, Procedure I, II, III Low Temperature;
MIL-STD-883E, F, G, H Method 1010.7, Condition A, B, C, and F, Thermal Shock;
RTCA DO-160D, E, F, G Section 4 and 5;
TIA/EIA 455-4C, High Temperature
18. Solar Radiation (Sunshine)
ASTM G154-12a;
BS EN 50130-5:11;
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5 : Environmental Test Methods;
MIL-STD-810C, D, E, F, G Method 505.1, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810C, D, E, F, G Method 505.1, Procedure II;
IEC 60068-2-5:75; Part 2-5: Tests – Test Sa;
IEC 60068-2-5:10;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Solar Radiation;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Solar Radiation;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Solar Radiation;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Solar Radiation;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Solar Radiation;
IS 10236 Part 16;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev.2 Test Number 25
19. Temperature and Humidity
ASTM D4169-14;
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5: Environmental Test Methods;
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006;
DET NORSKE VERITAS (DNV) STANDARD FOR CERTIFICATION NO. 2.4: ENVIRONMENTAL TEST SPECIFICATIONFOR INSTRUMENTATION ANDAUTOMATION EQUIPMENT (April 2006);
EIA/JEDEC Standard EIA/JESD22-A101-B;
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 12 Damp Heat, Steady State (Operational);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 13 Damp Heat (Endurance);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 14 Damp Heat Cycling (Operational);
EN 50130-5:1999 Section 15 Damp Heat Cycling (Endurance);
ETSI 300-019-2-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8;
GM 9123P;
GR-63-CORE, Issue 1, Paragraph 5.1.1.3, Humidity;
GR-63-CORE, Issue 1, 2 and 3, Paragraph 5.1.2, Humidity;
GR-1221-CORE, Paragraph 6.2.5 and 6.2.8, Humidity;
IEC 68-2-3, Test Ca, Humidity replaced by IEC 60068-2-78;
IEC 68-2-30, IEC 60068-2-30, 3ed 2005, Test Db, Humidity;
IEC 68-2-38 led 1974,Test Z/AD, Humidity;
IEC 60068-2-56, Test Cb, Humidity superseded by IEC 680068-2-78:2001;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Humidity/Damp Heat;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Humidity/Damp Heat;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Humidity/Damp Heat;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Humidity/Damp Heat;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Humidity/Damp Heat;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IEC 60721-3-2;
IS 10236 Part 4 – Damp Heat;
IS 10236 Part 5 – Damp Hear (Cyclic);
ISTA 1A- 2014, ISTA 2A-2011, ISTA 3A-2008;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 10, 27;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-STD-202F Method 103B, Conditions A, B, C, and D, Humidity;
MIL-STD-202F Method 106E, Humidity;
MIL-STD-202G Method 103B, Conditions A, B, C, and D, Humidity;
MIL-STD-202G Method 106G, Humidity;
MIL-STD-810C Method 507.1, Procedures I, II, III, IV, and VI;
MIL-STD-810D Method 507.2, Procedures I, II, and III;
MIL-STD-810E Method 507.3, Procedures I, II, and III;
MIL-STD-810F Method 507.4, Procedure I;
MIL-STD-810G Method 507.5 Procedures I, and II;
MIL-STD-883E Method 1004.7;
MIL-STD-883F Method 1004.7;
MIL-STD-883G Method 1004.7;
MIL-STD-883H Method 1004.7;
MIL-STD-883J Method 1004.7;
MIL-STD-1344A Method 1002.2, Type I, Conditions A, B, C, and D;
MIL-STD-1344A Method 1002.2, Type II, and III;
RTCA DO-160C,D,E,F,G Section 6;
TIA/EIA 455-5C, Method A, Conditions A, B, C, D and E, Humidity;
TIA/EIA 455-5C, Method B and C, Humidity;
20. Vibration
ASTM D999, ASTM D999-96, D999-2001 Method Al, B, C, Sine Vibration;
ASTM D4169-14;
ASTM D4728, ASTM D4728-95, D4728-2006 RandomVibration;
BRB/LU Ltd /RIA SPECIFICATION No 20:1988 (Testing for Railway Vehicles);
“DET NORSKE VERITAS (DNV) STANDARD FOR CERTIFICATION NO. 2.4
: ENVIRONMENTAL TEST SPECIFICATIONFOR INSTRUMENTATION
ANDAUTOMATION EQUIPMENT (April 2006);”
GR-63-CORE, Paragraph 5.4.2, Sine Vibration;
GR-63-CORE, Paragraph 5.4.3, Sine Vibration;
GR-1221-CORE, Paragraph 6.2.2, Sine Vibration;
General Motors Engineering Standards GM 9123P;
General Motors Engineering Standards GM 3155;
IEC 68-2-6, IEC 60068-2-6, Test Fc, Sine Vibration;
IEC 68-2-34:73 AMD 1 83, Test Fd, Random Vibration;
IEC 68-2-36, Test Fdb, Random vibration superseded by IEC 60068-2-64;
IEC 68-2-64 1993 COR 1 1993, Test Fh, Random Vibration;
IEC 60601-1-11;
IEC 60721-4-1:2001+A1:03 – Sine Vibration;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Random Vibration;
IEC 60721-4-2:2001+A1:03 – Sine Vibration;
IEC 60721-4-3:2001+A1:03 – Sine Vibration;
IEC 60721-4-4:2001+A1:03 – Sine Vibration;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Random Vibration;
IEC 60721-4-7:2001+A1:03 – Sine Vibration;
IEC 60721-3-2;
IS 10236 Part 11;
ISTA 1A-2014, ISTA 2A-2011, ISTA 3A-2008;
JIS E 3014: 1999 Part of Railway signal – Vibration Test Methods;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev. 2 Test Number 4, 28;
MIL-B-49430, Paragraph 4.8.6, Sine Vibration;
MIL-B-49458C (ER), Paragraph 4.8.6, Sine Vibration;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-PRF-49471B (CR), Paragraph 4.7.6;
MIL-STD-202F Method 201A, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-202F Method 204D, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-202F Method 214 Condition I, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-202F Method 214 Condition II, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-202G Method 201 A, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-202G Method 204D, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-202F Method 204D, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, Sine Vibration;
“MIL-STD-202F Method 214 Condition I, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H,
J, K, Random Vibration;”
MIL-STD-202F Method 214 Condition II, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-202G Method 201 A, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-202G Method 204D, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, Sine Vibration;
“MIL-STD-202G Method 214 Condition I, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H,
J, K, Random Vibration;”
MIL-STD-202G Method 214 Condition II, Test Conditions A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD 167 -1A:05 – Vibrations of Shipboard Equipment;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure I, Curve AR-L, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure 1, Curve B, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure 1, Curve M, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure IA, Figure 514.2-2A, Random Vibration
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure IIA, Figure 514.2-4, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure IIB, Figure 514.2-4, Random Vibration;
“MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure V, VI, VII,
Figure 514.2-4A, Sine & Random Vibration;”
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure VIII, Curve V, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure VIII, Curve W, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810C Method 514.2, Procedure VIII, Curve Y, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810D Method 514.3, Category 1, Procedure I, Random Vibration;
EIA/JEDEC STANDEARD EIA/JESD22 –B103-B;
MIL-STD-810D Method 514.3, Category 10, Procedure 1, Sine & Random Vibration
MIL-STD-810D Method 514.3, Category 4, 5, 6, 7B, 7C, 8, 9, Procedure I, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810D Method 514.3, Category 7A, Procedure IV, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810D Method 519.3, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810E Method 514.4, Category 1, 4, 5, 6, 7B, 7C, 8, 9, Procedure I, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-8 I0E Method 514.4, Category 10, Procedure 1, Sine & Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810E Method 514.4, Category 7A, Procedure IV, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-8 1OE Method 519.4, Gunfire Vibration;
MIL-STD-810E Method 521.1;
MIL-STD-810F Method 514.5 Category 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 25, Procedure I, Random Vibration;
“MIL-STD-810F Method 514.5, Category 15, 17, 18, 19, Procedure IV, Random
Vibration;”
MIL-STD-810F Method 514.5, Category 20, Procedure III, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-8 10F Method 514.5, Category 24, Procedure 1, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-810F Method 519.5, Gunfire Vibration;
MIL-STD-810F Method 521.2;
MIL-STD-810F Method 528, Shipboard Equipment;
MIL-STD-810G Method 514.6, Category 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 221, 22, 23, 24, 25, Procedure I, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810G Method 514.6, Category 15, 17, 18, 19, Procedure IV, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810G Method 514.6, Category 20, Procedure III, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-810G Method 519.6, Gunfire Vibration;
MIL-STD-810G Method 521.3;
MIL-STD-883E, F, G, H, J Method 2005.2, Test Conditions A, B, C, Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD-883E, F, G, H, J Method 2026, Condition 1, Test Conditions A, B, C, E, F, G, H, J,K, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD-883E, F, G, H, J Method 2026, Condition 11, Test Conditions A, B, C, E, F, 0, H, J, K, Random Vibration;
MIL-STD- I 344A Method 1015, Condition B (Group III) Sine Vibration;
MIL-STD- I 344A Method 2005.1, Conditions I, II, III, IV, V (A, B, C, D, E, F, G,H, J, K), VI (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, J, K);
RTCA DO-160D Section 8;
RTCA DO-160E Section 8;
RTCA DO-160F Section 8;
RTCA DO-160G Section 8;
TIA/EIA 455-1 IB, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition I, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1113, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition 11, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1113, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition III, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-11B, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition IV, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1113, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition IV, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1113, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition VI, Random Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1 IB, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition VII, Random Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1 I C, TIAIEIA 455-11C, Condition I, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-11C, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition II, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1 IC, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition III, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-11 C, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition IV, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-11C, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition IV, Sine Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-1 1C, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition VI, Random Vibration;
TIA/EIA 455-11C, TIA/EIA 455-11C, Condition VII, Random Vibration;
QM-333 Paragraph 12.0, Category A, B, C, D, Sine Vibration;
UL-1642, Paragraph 15, Sine Vibration;
UN Transport of Dangerous Goods, Test T.2, Sine Vibration;
ISO 10651-3 Lung Ventilators Medical Use Part 3;
ISO 14708-1:200 (E), Section 4: Protection against mechanical hazards;
BS EN 50155:2007;
BS EN 61373:1999;
DEF-STD 00-35 part 3;
DEF-STD 00-35 part 5;
ETSI 300-019-2-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8;
NATO AECTP-400 Edition 3;
BMW Group GS95003-1;
ASTM D999, Method A1, B, C, Sine Vibration;
ASTM D999, ASTM D999-96, D999-2001 (Method A1, B, C, Sine Vibration);
ASTM D4728, Random Vibration;
ASTM D4728, ASTM D4728-95, D4728-2006 Random Vibration;
EN 50130 Section 22,23 Vibration, Sinusoidal;
EN 50130:1999 Section 22 Vibration, Sinusoidal (Operational);
EN 50130:1999 Section 23 Vibration, Sinusoidal (Endurance);
BS EN 50130-5:1999 Alarm Systems Part 5 : Environmental Test methods
21. HALT
Highly Accelerated Life Test (HALT);
Cold Temperature Steps;
Hot Temperature Steps;
Cold Start Test;
Temperature Cycling;
Random Vibration-3 axis;
Temperature & Vibration Combined Cycling;
Temperature Measurements
22. HASS
Highly Accelerated Stress Simulation (HASS); Stress Profile Definition; Analyzing POS Stage; Mounting Jig Assembly;
Running Multi-Tester Jig; Set-up for Mass Production; Temperature & Vibration Combined Cycling
23. IR Imaging
Using Inframetrics PM920 Thermacam IR Camera Using Method:
ThermaCAM Hand-held IR Imaging Radiometers Operating Instructions
24. Sand & Dust
DEF STAN 00-35, Part 3, Issue 4:2006 Chapter 3-25 Test CL25;
IEC 60529-2001 COR 1 2003, Degrees of Protection provided by Enclosures
(IP Code) Degrees of protection (IP-Code), IP5X,6X;
IS 10236 Part 13;
JSS 55555:2000 Rev.2 Test Number 14;
MIL-DLT-62547C(AT);
MIL-STD-810 C, D, E, F, G, Method 510, Procedures I, II and III;
RTCA DO-160 C,D,E,F,G, Section 12, Procedure II